DanzArTe – Emotional Wellbeing Technology comprises a new scientifically and clinically validated protocol (thanks to the collaboration with the Galliera Hospital of Genoa, Geriatric Care Unit) and a cost-effective technological platform for the treatment of older adults at risk of frailty and for the active enjoyment of artistic content.
DanzArTe involves interaction with visual content (visual arts artworks) and sound content (interactive sonification): an innovative protocol that supports active experience (aesthetic resonance) with art underpins an interactive system for physical activity and cognitive stimulation adapted to the needs of frail or at-risk older adults. Dancing Art as physical activity and as a cognitive memory-training exercise to rediscover oneself through dance (Dancing Art, dancing You).
Through DanzArTe, participants are brought into particularly intense contact with the world of art and discover new ways of enhancing local cultural heritage within an inclusive and rehabilitative dimension, defining a concept of health understood globally as the reconstitutable harmony in the relationship between the physical, intellectual, emotional, and social functions of the person.
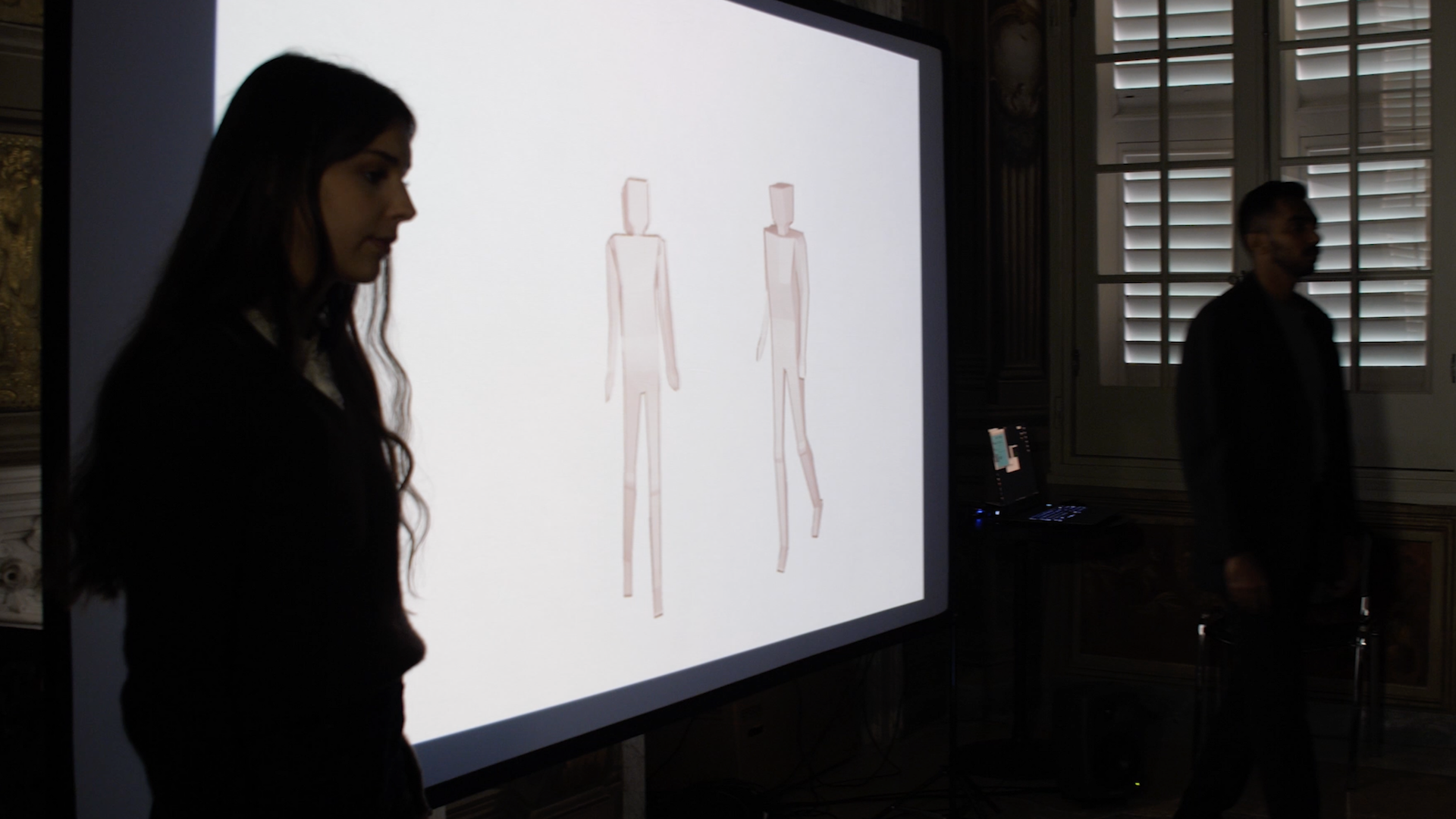
Through artificial intelligence technologies and real-time analysis and sonification of movement, DanzArTe interactively guides participants, individually or in groups, to reconstruct the gestural contents (and their consequent emotional values) of ancient works of sacred art, through simple movements and revealing manipulations of sounds and images.
DanzArTe’s emotional wellbeing technology (multimodal and interactive) transforms “physical contact” with the artwork into a new collective amateur practice which, by emotionally engaging movement and memory, creates a compelling community experience.
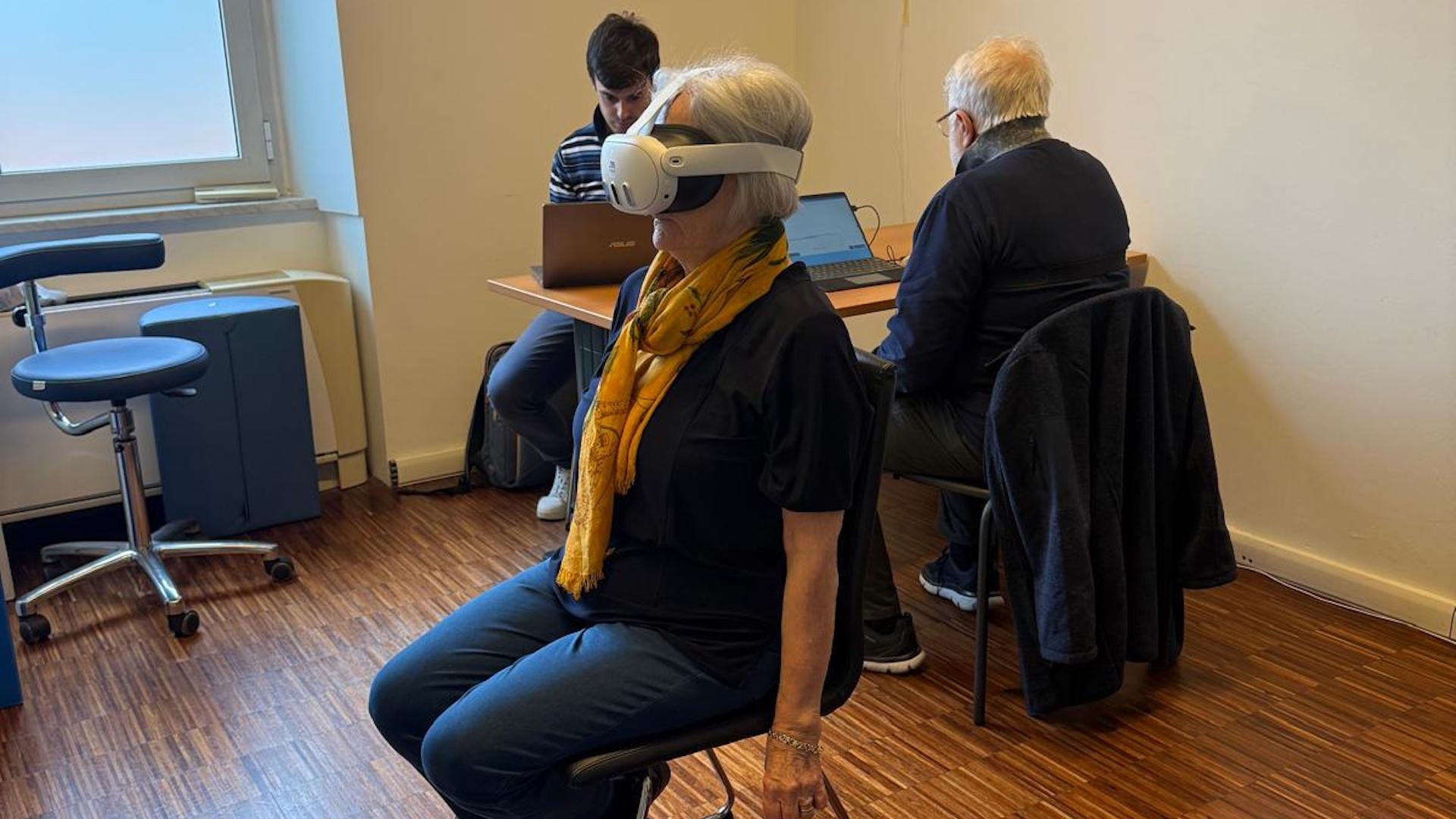
The project has been tested and implemented in 10 residential care facilities (RSA) in Liguria and Piedmont, at the international rehabilitation center Villa Beretta (Lecco), and in senior community centers. It has also extended into museum institutions across Liguria and Piedmont, including pilot activities at the Diocesan Museum of Genoa and at Palazzo Reale.
The DanzArTe project originated as one of the four pilot projects of the Cultural Wellbeing Lab of Compagnia di San Paolo. The artificial intelligence technologies for real-time movement analysis and sonification derive from results achieved within the EU H2020 FET PROACTIVE project EnTimeMent.
Since 2023, within the RAISE project, DanzArTe has been further developed and expanded for the active enjoyment of cultural content and artworks from a cultural wellbeing and audience engagement perspective.
The outcomes of this new phase of the project were presented and tested at Galliera Hospital (August 2025) within Spoke 2 of the RAISE project, and in Spoke 1 pilot activities with the public during Alzheimer Fest (Chiavari, September 2025) and at the event Real Inclusion: when the home becomes a museum and the museum becomes home again, December 3, 2025, at Palazzo Reale in Genoa, on the occasion of the International Day of Persons with Disabilities. These activities were carried out by InfoMus–Casa Paganini within Spoke 1.
Within this framework, DanzArTe emerges as an innovative and replicable model for integrating art, technology, and care, capable of generating cultural, social, and health value, and of making a significant contribution to the goals of inclusion, wellbeing, and territorial impact promoted by the RAISE project.
Cover image
Photo author (video frame): Marzio Cardellini (Bluframe)
Credits: RAISE